Understanding Hydroponic vs. Industrial Chillers
Defining Hydroponic Chillers: Purpose and Components
As mentioned earlier, hydroponic chillers are used to regulate the perfect temperatures for plants’ growth performed through water-based methods. These types of chillers have specific components, such as compressors, evaporators, and condensers, which are properly modulated to be energy efficient while keeping up with the water discipline. It is common knowledge that when the temperatures in the hydroponics are too hot, it can kill the plants or severely slow down the development leading to low yields. Furthermore, such chillers are tremendous components of NFT and DWC because the systems water and the plants’ oxygenation need very specific modulating temperatures and procedures.
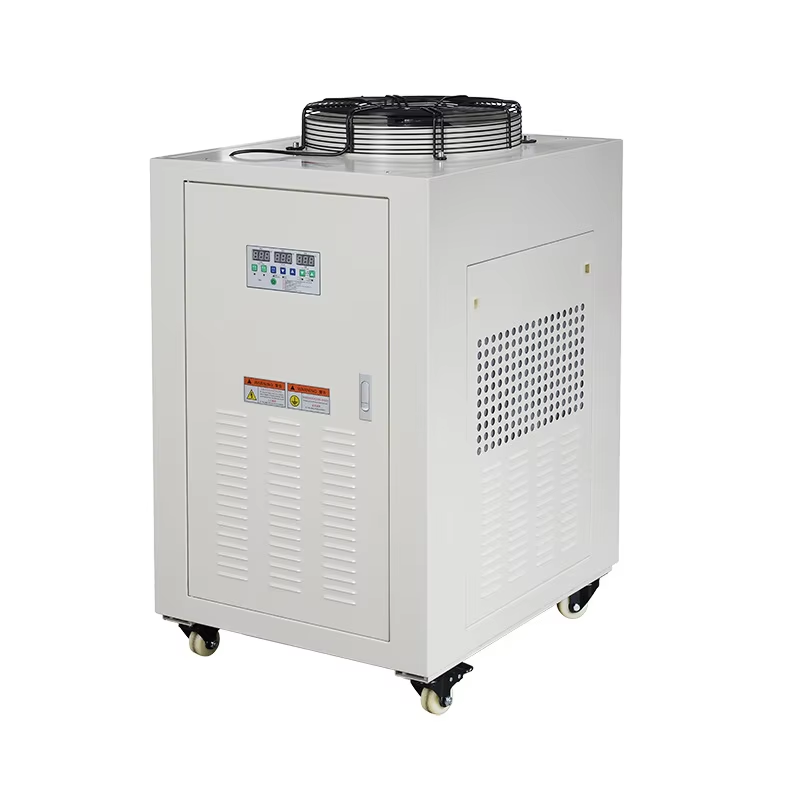
Industrial Chillers: Core Mechanisms and Applications
A periodic refrigeration or industrial cooling chiller that rejects the heat extracted from the process is typically used to cool down these processes. Such systems frequently utilize cooling towers or dry-coolers for efficient heat removal. Industrial chillers are used on large-scale and are cooled with the help of water and use refrigerant for the endothermic process. Efficient operation of these industries demands high heat extraction. Knowledge of the principles of operation of industrial chillers is necessary to achieve its best use in different applications for the sake of higher efficiency and lower cost energy.
Key Overlaps in Cooling Technology
Although used in different contexts, hydroponic and industrial chillers apply the same thermodynamic concept, mainly in terms of heat transfer and fluid mechanics. The operation of both systems depends on the refrigerant and heat exchanger, which are the key to achieving the required cooling. These parallels indicate that there may be opportunities for cross-sectorial innovations in the design of their operational approaches. The mutually technology supports that technology in one field may be utilized as a seed of innovation in the other and thus there could be significant benefit in efficiency for multiple application areas in the thermal management systems.
Cooling Methods: Refrigeration vs. Process-Specific Systems
The cooling approaches for both hydroponic and industrial chillers differ greatly due to the differing requirements of each application. Many hydroponic chillers use sophisticated cooling methods to achieve desired temperature levels, essential for the well-being of delicate plants. For instance, lettuce cultivated under hydroponic techniques might want the conditions of temperature to be tightly controlled in order to optimise growth as exemplified by the cited Purdue University study. On the other hand, the process fluid and cooling water used in industrial chillers are constantly cooled to the same temperature which are standard in the industry and fit many different types of applications. It is this flexibility that allows them to be used in the cooling of different manufacturing flows, ensuring that operations are productive. While hydroponic chillers zero in on exact control to enhance the plant's enzyme performance, our industrial chillers zero in on processing-specific cooling needs for maximum manufacturing efficiency.
Material Durability: Titanium vs. Industrial-Grade Components
Materials used also play a key role in ensuring the life-span and durability of chiller units for specific operating environments. When it comes to this, hydro chillers frequently use titanium or other anti-corrosive building to stand up to the increased cations in the water from the increased nutrient.Additional Resources tick the links.. Such materials inhibit deterioration and permit a long lifetime for the system, as observed in the optimization of lettuce growth in nutrient solutions. Industrial chillers, on the other hand, use steel or aluminum to provide longevity as well as versatility and durability across different settings and temperature needs. These material and construct specifications are vital for purchasers of a chiller system who require a system that's suited for their intended application, and which will provide years of reliable service.
Temperature Range Variations
Overall, hydroponic and industrial chiller temperatures followed different types of variation since they are meant to achieve varying goals. First, hydroponic chillers operate at very precise temperature ranges, such as between 18°C and 22°C, as supported by hydroponic articles. The very tight control is required to ensure that plants absorb the right nutrients because plant studies support this view. Additionally, such hydroponic chillers achieve the required growth cycle and enzymatic activity when coupled with heating valves and heat rejection controls. Conversely, industrial chillers experienced more variation since they worked within more than 10°C to above 30°C ranges. Industrial chiller flexibility is required to address variable industrial processes. Hence, specific chiller types require being chosen for any cooling application.
Application Scenarios: Where Each Chiller Excels
Hydroponic Chillers in Agriculture and Cold Plunge Systems
Finally, the use of hydroponic chillers is crucial for agricultural installations, such as greenhouses, to provide the perfect temperature for the plants to grow at all times. It allows the plants to absorb nutrients even under high light demand in critical nutrient uptake periods, which are necessary for the high yield. Moreover, introduced cold plunge systems that are becoming a trend in the sports and wellness markets require the optimal cold that is possible only with a chiller. The explanation of the cold plunge application, in this case, is the necessary relaxation of muscles and the body in general should be provided with precise temperatures possible with a chiller. In other words, the chiller may be adapted to a wide range of niche uses where low-temperature stability is essential, which is evident during the realization of a particular cold plunge.
Industrial Chillers in Manufacturing and HVAC
Overall, industrial chillers cannot be ignored considering their role in HVAC systems. The need to provide cool environments within some of the largest structures means that the role these devices play can never be understated. They are vital for most manufacturing processes since the associated operations generate some heat that could be harmful as far as the quality of products and efficiency of machines are concerned. Moreover, the fact that industrial chillers can handle high cooling loads and are suitable for the vast vital industrial frameworks necessitates their importance. Ideally, these devices confirm that they are not only essential for the established industrial systems but also the potential of emerging sectors.
Niche Uses: Ice Bath Chillers and Water Cooling for Labs
HydroSiesta Ice bath chillers are specifically designed for athletes recovery methods, Hydroponic chiller ideas, hook up the ability to chill baths to lower temperatures than you can afford to leave your warehouses AC system set at. In labs, chillers provide water cooling needed to cool heatusp in equipment such as autoclaves, baths, pasteurizers, and fermenters and thus to keep equipment and processed materials at the correct temperature. The versatility of hydroponic and industrial chillers is demonstrated in these two examples. Their uses are wide ranging from cold plunges in aiding athletics for recovery to providing controlled atmospheres for scientific research, so versatility is key. This flexibility indicates that there is great possibility for further innovation and adoption across multiple sectors.
Performance Metrics and Efficiency
BTU Requirements for Hydroponic vs. Industrial Loads
The voltage of the chillers is determined by BTU ; thus, it is imperative to understand the energy and chiller’s capacity requirements to determine how much power you need to install. The difference results from how the load was calculated, since the systems are different. Hydroponic systems are small and more suitable for controlled tanks. They range from 3,000 to 15,000 BTUs depending on the size of the farming plot. Precise determination ensures no power wastages and the correct conditions for the growth of plants.
By contrast, commercial chillers must bear very heavy loads and require BTU ratings of 100,000 or higher. This tremendous difference serves to illustrate the massive cooling capabilities of the industrial chiller, which is indispensable in process industries where extremely high temperatures can be detrimental to machine operation or product quality. These industrial uses require durable construction to withstand heavy usage, and BTU factors are essential for chiller usage determination and specification.
Energy Consumption Comparisons
The ratio of energy use between hydroponic and factory chillers differs markedly, that would mostly depend on running hours and construction. Hydroponic chillers are designed for specific cooling that typically end up using less energy per unit to produce. This level of efficiency also makes them particularly well suited to agricultural facilities, like environmental rooms, where keeping energy costs in check, even while maintaining tight control of temperatures for better plant growth, is a priority.
Conversely, industrial chillers are often highly energy consuming, because of their large scale. There may be added features though, such as variable speed drives that set motor speed according to cooling load, in that case achieving a high overall efficiency. This ability results energy saving in cases which operational needs change, and proves the necessity of these technologies in the field of industrial energy consumption control.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While both of agricultural and industrial energy consumption rises, the environmental effects and sustainability of hydroponic cooler against industrial cooler is becoming more and more important. Hydroponic systems can also use environmentally friendly refrigerants, and have lower energy inputs, which serves the broader goal of more sustainable agriculture. This is a mode of operation that is not only good for the environmental health, also good for producers to tap into the expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
On the other hand, the pressure is increasing for industrial chiller systems to adopt greener technologies with increasing regulations and corporate social responsibilities schemes. There are many industrial establishments that are introducing the concept of new refrigerants and energy-efficient designs to minimize the effect caused on the environment. As businesses work through these challenges, maintaining efficient and sustainable chiller systems isn’t just to satisfy regulation, but rather a strategic route to addressing long term operational sustainability and stewardship of the environment.
Choosing the Right Chiller for Your Needs
Assessing Cooling Capacity and System Size
Before buying a chiller it is important to know its cooling capacity, usually expressed in tons or BTUs. This number is vital to make certain that the chiller you choose can meet the heat removal needs and requirements of your particular set-up. You should be able to accurately judge the operational demands of products; a hydroponic chiller will be adequate for smaller agricultural operations but larger commercial or industrial operations will warrant a substantial industrial chiller. If the chiller capacity isn't matched to system size, it can waste or struggle to produce results for you with either excess effort or too much/ too little heat removed in the concern systems.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
It is imperative that you weigh the cost when deciding the type of Chiller that is right for your farm between hydroponic and industrial chillers. It is important to consider the high initial investment against potential long-term saving of energy and maintenance. Chillers for hydroponics are usually less expensive from the getgo, and they all promise tremendous energy savings with all their fancy new tech, so they can be a great option for a tighter operation. In contrast, industrial chillers may cost more upfront, but can bring down the running costs significantly over the years – particularly when used in mass scale applications, enabling them to use economies of scale.
Maintenance and Operational Demands
Chiller requirements Understanding the maintenance and operations are paramount when choosing the right chiller. Also, hydro chillers are typically kept for long without the need of maintenance, so they can be great if you'd rather not bother with maintaining the system often. On the other hand, industrial chillers, which are often more complicated, might need to be maintained every few months because of heavy duty usage. This has the potential to make significant differences in the operating life as well as in the costs. These requirements should be taken into account when choosing a chiller, so that you can handle the necessary maintenance without paying extensively on labor costs.