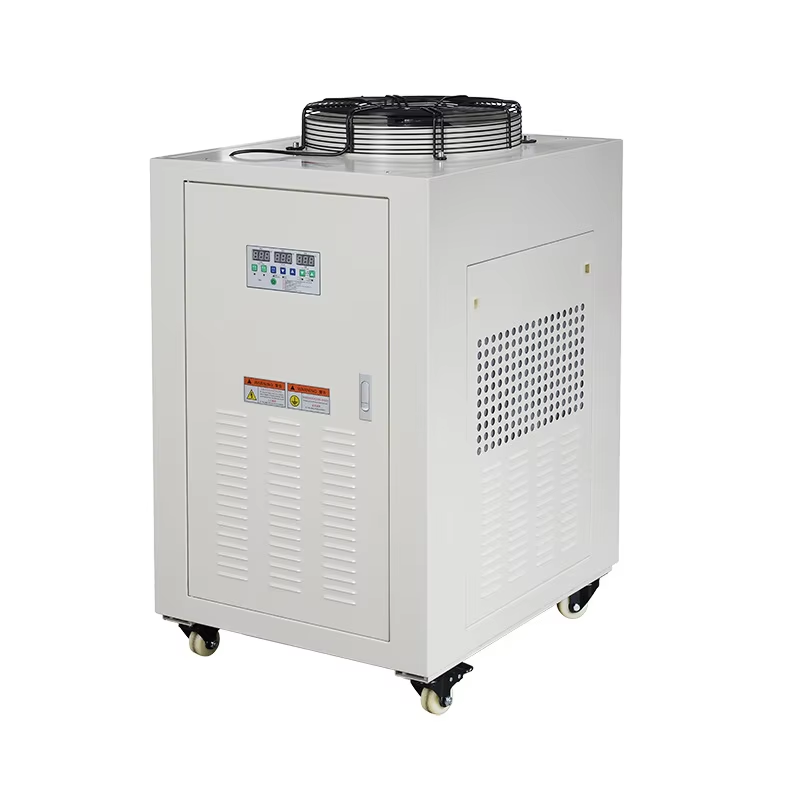
Razumevanje razlika između hidroponskih i industrijskih hlačaca
Definisanje hidroponskih hlačaca: namena i komponente
Kao što je već rečeno, hidroponski hlađači se koriste za regulisanje savršenih temperatura za rast biljaka koji se vrši metodom baziranom na vodi. Ovi tipovi hlađača imaju specifične komponente, kao što su kompresori, evaporatori i kondenzatori, koji su pravilno modulisani kako bi bili energije uštedljivi dok istovremeno održavaju vodeni redosled. Poznato je da visoke temperature u hidroponici mogu ubiti biljke ili znatno usporiti njihov razvoj, što dovodi do niskog uznašaja. Nadalje, takvi hlađači su ogromni deo NFT i DWC sistema, jer voda u sistemu i oksigenacija biljaka trebaju vrlo specifično regulisane temperature i procedure.
Industrijski hlači: Glavni mehanizmi i primene
Periodyčno se koristi hlađač za refrigerciju ili industrijsko hlađenje koji odbacuje toplinu izvučenu iz procesa kako bi se ohladili ti procesi. Takvi sistemi često koriste hlađalne kule ili suve hlađalice za efikasno uklanjanje topline. Industrijski hlađači se koriste na velikom skalu i hlađaju se pomoću vode, a koriste hlađajuću tvari za endotermični proces. Efikasna radnja ovih industrij zahteva visoku ekstrakciju topline. Znanje principa rada industrijskih hlađača je neophodno da bi se postigao najbolji njegov korisak u različitim primenama uz cilj veće efikasnosti i nižeg troška energije.
Кључне преклапања у технологији хлађења
Iako se koriste u različitim kontekstima, hidroponski i industrijski hlačci primenjuju isti termodinamički koncept, glavno u odnosu na prenos toplote i mehaniku fluida. Rad oba sistema zavisi od hladnog sredstva i toplinskog zamjenika, što su ključni čimbenici za postizanje potrebnog hlađenja. Ove paralele ukazuju da postoje mogućnosti za inovacije između sektora u dizajnu njihovih operativnih pristupa. Uzajamna tehnološka podrška znači da tehnologija iz jedne oblasti može biti iskorišćena kao osnova za inovacije u drugoj, a time bi se moglo ostvariti značajno povećanje efikasnosti u više oblasti primene u sistemima upravljanja toplinom.
Metode hlađenja: refrigercija vs. sistemи specifični za proces
Pristup hlajenju za hidroponiku i industrijske hlačice značajno se razlikuje zbog različitih zahteva svake primene. Mnoge hidroponične hlačice koriste sofisticirane metode hlajenja kako bi dostigli željene nivoje temperature, što je ključno za dobrobit osetljivih biljaka. Na primer, salata koja se uzgaja pomoću hidroponskih tehnika može da zahtevaju strogo kontrolisanje temperature kako bi se optimizovao rast, kao što pokazuje studija s Univerziteta u Purdu. S druge strane, procesna tekućina i voda za hlajenje koja se koristi u industrijskim hlačicama stalno se hladi na istu temperaturu koja je standardna u ovom sektoru i odgovara mnogim različitim vrstama primena. Pogodnost koju pružaju omogućava im da se koriste za hlajenje različitih proizvodnih tokova, osiguravajući da operacije budu produktivne. Dok se hidroponične hlačice fokusiraju na tačnu kontrolu kako bi poboljšale performansu enzima biljaka, naše industrijske hlačice fokusiraju svoje potrebe za hlajenje specifično za obradu, štedeći maksimalnu efikasnost u proizvodnji.
Trajanost materijala: Titan vs. industrijski komponenti
Materijali koji se koriste takođe igraju ključnu ulogu u osiguranju životnog veka i trajnosti jedinica hlađenja za određene radne okruženja. Kada je riječ o tome, hidro hlačere često koriste titan ili druge protuproraštice materijale kako bi se uprotili povećanom sadržaju kationa u vodi uzrokovanom dodavanjem nutritivnih sastojaka. Dodatni resursi potvrđuju veze... Takvi materijali sprečavaju deteroraciju i omogućavaju dug život sistemima, kao što se može primetiti u optimizaciji rasta salaata u nutritivnim rešenjima. Industrijska jedinica hlađenja, s druge strane, koristi ocel ili aluminijum kako bi obezbedila dugogodišnju upotrebu, kao i fleksibilnost i trajnost u različitim okruženjima i potrebama temperature. Ove specifikacije materijala i konstrukcije su ključne za kupce sistema hlađenja koji traže sistem prilagođen njihovoj nameni, a koji će pružati godinama pouzdane usluge.
Variranja u opsegu temperature
Uopšte, temperature hidroponskih i industrijskih hlađača prate različite vrste varijacija jer su namenjene postizanju različitih ciljeva. Prvo, hidroponski hlađači rade u veoma preciznim temperaturnim opsege, kao što je između 18°C i 22°C, kako potvrđuju članci o hidroponici. Potrebna je vrlo snažna kontrola kako bi se osiguralo da biljke apsorbiraju odgovarajuće nutritivne sastojke, što podržava istraživanja biljaka. Pored toga, takvi hidroponski hlađači dostižu potrebni ciklus rasta i enzimsku aktivnost kada su kombinovani sa vreličkim ventilima i kontrolama odbacivanja topline. S druge strane, industrijski hlađači imaju veću varijabilnost jer rade u opsegu od više od 10°C do iznad 30°C. Fleksibilnost industrijskih hlađača je neophodna kako bi se prilagodila promenljivim industrijskim procesima. Stoga, za bilo koju hlađenu primenu treba birati odgovarajući tip hlađača.
Scenariji primene: Gde svaki hlač iznjačava
Hidroponski hlači u poljoprivredi i sistemima za hladno toplovanje
Na kraju, korišćenje hidroponskih hlačara je ključno za agrarske instalacije, kao što su teplice, kako bi se obezbedila savršena temperatura za rast biljaka uvek. Omogućava biljkama da apsorbiraju štoviše čak i pod visokim zahtevima svetlosti u kritičnim periodima uzimanja štovišta, koji su neophodni za visoku proizvodnju. Takođe, uvode se sistemi hladnih kupatila koji postaju trend u sportskim i wellness tržištima, a koji zahtevaju optimalnu hladu koju je moguće postići samo sa hlačarom. Objasnjenje primene hladnog kupatila, u ovom slučaju, jeste neophodna relaksacija mišića i tela opšte koja treba da se obezbedi preciznom temperaturom koju omogućava hlačar. Drugim rečima, hlačar može biti prilagođen širokom rasponu specijalizovanih upotreba gde je stabilnost niske temperature esencijalna, što je očigledno tijekom realizacije određenog hladnog kupatila.
Industrijski hlači u proizvodnji i HVAC
Uopšte, industrijski hlačići ne mogu biti zanemareni uzimajući u obzir njihovu ulogu u sistemima HVAC. Potreba za pružanjem hladnijeg okruženja unutar nekih od najvećih struktura znači da se uloga koju ovi uređaji igraju nikada ne može umaniti. Oni su ključni za većinu proizvodnih procesa, jer povezane operacije generišu neku količinu topline koja bi mogla biti štetna u pogledu kvaliteta proizvoda i efikasnosti mašina. Pored toga, činjenica da industrijski hlačići mogu da obrade velike hlađene opterećenja i da su prikladni za širok spektar ključnih industrijskih okvira potvrđuje njihovu važnost. Idealno, ovi uređaji potvrđuju da nisu samo esencijalni za postojeće industrijske sisteme, već i za potencijal rastućih sektora.
Специјалне употребе: Хилери за ледене бање и водено хлађење у лабораторијама
HidroSiesta ledeni kuhaci su posebno dizajnirani za metode oporavka atleta, ideje za hidroponičke kuhace, omogućuju povezanost sposobnosti da hladite kupe do nižih temperatura nego što možete ostaviti sistem klimatizacije u skladištu. U laboratorijima, kuhaci pružaju hlađenje vode potrebno za hlađenje topline u opremi kao što su aotoklave, kupe, pasteurizatori i fermenteri, čime se osigurava da je oprema i procesirani materijal na tačnoj temperaturi. Versatilnost hidroponičkih i industrijskih kuhaca ilustruju ova dva primera. Njihova upotreba je širokog spektra, od hladnih ponora koji pomazu u oporavku atleta do pružanja kontrolisanih atmosfera za naučna istraživanja, tako da je versatilnost ključna. Ova fleksibilnost ukazuje na veliku mogućnost daljeg inoviranja i primene u više sektora.
Performanse i efikasnost
Zahtevi BTU za hidroponične i industrijske opterećenja
Napon hlačnog uređaja određen je BTU-om; stoga je ključno razumeti zahteve energetske potrošnje i kapaciteta hlačnog uređaja kako bi se utvrdilo koliko snage treba instalirati. Razlika izvodi se iz načina na koji je opterećenje izračunato, budući da su sistemi različiti. Hidroponski sistemi su mali i prilagođeniji kontrolisanim bazenima. Obrasci su od 3.000 do 15.000 BTU-a, zavisno od veličine poljoprivrednog terena. Tačno određivanje osigurava da neće doći do gubitaka snage i da postoje prave uslove za rast biljaka.
U protivnosti, komercijalni hlači moraju da nose veoma teške opterećenja i zahtevaju BTU rejting od 100.000 ili više. Ova ogromna razlika služi da ilustruje masovne mogućnosti hlađenja industrijskog hlača, koji je neophodan u procesnim industrijama gdje su ekstremno visoke temperature štetne za rad mašina ili kvalitet proizvoda. Ove industrijske upotrebe zahtevaju trajnu konstrukciju kako bi pretrpela tešku upotrebu, a BTU faktori su ključni za određivanje i specifikaciju upotrebe hlača.
Uporedbe potrošnje energije
Odnos upotrebe energije između hidroponskih i industrijskih hlačnica značajno se razlikuje, a to će uglavnom zavisiti od radnih sati i konstrukcije. Hidroponski hlačnici su dizajnirani za specifično hlađenje koje obično rezultira manjom potrošnjom energije po jedinici pri proizvodnji. Ovaj stepen efikasnosti čini ih posebno prilagođenim za poljoprivredne objekte, poput kontroliranih soba, gde je prioritet da se drže energetske troškove pod kontrolom, čak i dok se održava stroga kontrola temperature za bolji rast biljaka.
S druge strane, industrijske hlačnice često su vrlo potrošačke energetski zbog svoje velike dimenzije. Međutim, mogu imati dodatne funkcije, kao što su promenljivi brzinski pogoni koji postavljaju brzinu motora u skladu sa opterećenjem hlađenja, što u tom slučaju omogućava postizanje visoke ukupne efikasnosti. Ta sposobnost rezultira štednjom energije u slučajevima kada se menjaju operativni zahtevi, što dokazuje neophodnost ovih tehnologija u oblasti kontrole industrijske potrošnje energije.
Утицај на животну средину и одрживост
Dok porastaju oba, potrošnja energije u poljoprivredi i industriji, ekološki uticaji i održivost hidroponičnog hlačnog sistema u odnosu na industrijski hlačni sistem postaje sve važniji. Hidroponski sistemi takođe mogu koristiti ekološki prihvatljive freonove, a imaju niže energetske ulaze, što služi širem cilju održivije poljoprivrede. Ovo je način rada koji je ne samo dobar za ekološko zdravlje, već i dobar za proizvođače da ispunjavaju očekivanja potrošača svestranog prema ekologiji.
S druge strane, pritisak raste da industrijski sistemi hlađenja pređu na zelenije tehnologije uz porast regulacija i programa korporativne društvene odgovornosti. Mnoge industrijske ustanove uvode koncept nove generacije hladnjaka i energetski efikasne dizajne kako bi se smanjio uticaj na okoliš. Dok poduzetnici rade na ovim izazovima, održavanje efikasnih i održivih sistema hlađenja nije samo za ispunjavanje propisa, već i strategijski pristup rješavanju dugoročne operacijske održivosti i štitnje okoliša.
Izbor prave hlačice za vaše potrebe
Procena mogućnosti hlađenja i veličine sistema
Pre nego što kupite hlađač, važno je da znate njegovu mogućnost hlađenja, obično izraženu u tonama ili BTU-ovima. Ovaj broj je ključan kako biste bili sigurni da će hlađač koji birate moći da ispoštva potrebe i zahteve za uklanjanje topline vašeg specifičnog postavka. Trebalo bi vam biti moguće tačno procijeniti operativne zahtevе proizvoda; hidroponski hlađač će biti dovoljan za manje agrarske operacije, ali veće komercijalne ili industrijske operacije zahtevat će značajan industrijski hlađač. Ako se kapacitet hlađača ne podudara sa veličinom sistema, može izgubiti vrijeme ili teškoće u davanju rezultata zbog prekomjernog napore ili previše/malo topline koje se uklanja iz odgovarajućih sistema.
Analiza troškova: Početna investicija u odnosu na dugoročne štednje
Važno je da pretežite troškove prilikom odlučivanja koja vrsta hlađača je odgovarajuća za vašu farmu između hidroponskih i industrijskih hlađača. Ključno je razmotriti visoku početnu ulogu u odnosu na potencijalne dugoročne štednje energije i održavanja. Hlađači za hidroponsku proizvodnju su obično skuplji od početka, a sva obećanja ogromne štednje energije uz pomoć svoje modne nove tehnologije mogu biti odlična opcija za stroži posao. U protivnosti, industrijski hlađači mogu kostati više odmah, ali možda značajno smanje štete tokom godina – posebno kada se koriste u masovnim primenama, omogućavajući im da iskoriste ekonomiju skaliranja.
Zahtevi za održavanjem i radom
Zahtevi hlađenja. Razumevanje održavanja i operacija je ključno prilikom izbora odgovarajućeg hlađenja. Takođe, hidrohlađači se obično čuvaju dugo bez potrebe za održavanjem, pa mogu biti odlični ako ne želite da se bavite česte maintenanse sistema. S druge strane, industrijski hlađači, koji su često složeniji, možda će tražiti održavanje svakih nekoliko meseci zato što se koriste u teškom režimu rada. To može imati značajan uticaj na dužinu radnog veka kao i na troškove. Ovi zahtevi treba uzeti u obzir prilikom izbora hlađača, kako biste mogli da obavite neophodno održavanje bez previše trošenja novca na troškove rada.